What Is Bitcoin?

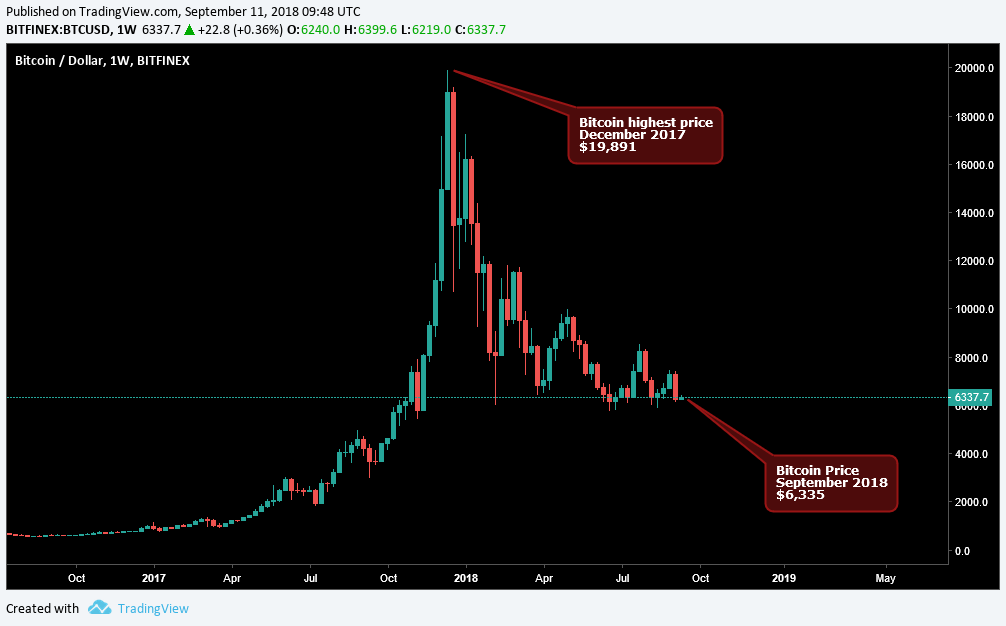
Since its inception in 2009, Bitcoin has been the talk of the internet due to its tremendous appreciation in value. During its debut in 2009, a single Bitcoin was worth less than $1; however, as of writing this article, Bitcoin’s price is $6,335. Keep in mind that in December 2017, Bitcoin hit a high of $19,891, and some exchanges quoted its price as high as $20,000. The underlying question is, what is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin’s highest price—December 2017
Bitcoin in a Nutshell
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that was pioneered in 2009 by a person or a group of persons under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin, denoted as BTC, was the first-ever cryptocurrency to be created. Bitcoin uses cryptography as its core technology—a technology model that guarantees anonymity and secure transactions. Bitcoin uses a process of mining, alternatively known as Proof of Work, to produce new Bitcoins.
Briefly, what is Bitcoin mining? Mining is a process in which Bitcoin transactions are verified and added to the blockchain through solving complex mathematical computations that involve the use of supercomputers. This process is free from any government intervention, and actual Bitcoin transactions are anonymous since Bitcoin users make their transactions through unique addresses. Newly mined Bitcoins are priced based on supply and demand.
Bitcoin Background
Bitcoin has its roots back in 2008. This is a period during which the world was recovering from the financial crisis said to have been specifically caused by the banks. The ripple effect was felt everywhere; the stock market lost a great deal, jobs were lost, and businesses closed. It’s from this mess that Satoshi, who created Bitcoin, is said to have come up with the idea of a decentralized money system that was free from manipulation by banks, governments, or any person. Satoshi spent the whole of 2008 writing the 31,000-line code that would later become the Bitcoin source code.
In August 2008, Satoshi registered the domain name Bitcoin.org and later, on October 31, 2008, released the Bitcoin original white paper. The white paper detailed exactly what is Bitcoin. From the onset, Satoshi had the idea of doing away with the existing trust-based monetary exchange system, wanting to adopt an electronic money system based on cryptographic proof.
The white paper described Bitcoin as a mathematical problem that has 21 million feasible solutions. The solutions are spread, and the last solution could only be arrived at in the year 2041. This would keep excess coins from coming into circulation, thereby preventing inflation. Each time the mathematical problem gets solved, a new block is added to the Blockchain, and the ones solving them (miners) would be rewarded with Bitcoin.
So when did Bitcoin start? On November 9, 2008, Satoshi released the source code to the public and registered the project at SourceForge.net. Later, on January 3, 2009, Satoshi mined the first 50 Bitcoins, also known as the genesis block. Since then, Bitcoin mining has continued, and as of 2018, there have been over 17 million Bitcoins mined out of the total possible 21 million coins.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
Bitcoin uses cryptography and the blockchain concept to process transactions and mining. For a Bitcoin user to make a transaction, they will need to have a public address. The addresses are interconnected, forming a network of addresses, which in a broader view is referred to as a public ledger.
For a transaction to happen, it has to be broadcast on the public ledger for verification. For instance, say John wants to send 1 Bitcoin to Jane, John’s transaction will be broadcast to other addresses in the network. These addresses will check whether John has 1 BTC and whether he is the owner. At that moment, the transaction status is unconfirmed.
For this part, we’ll need to go into more detail in answering the question, “what is Bitcoin?” To successfully make the payment, network participants called miners will have to verify the transaction. Miners bundle unconfirmed transactions through a rigorous computer process that tries to arrive at a solution to the mathematical problem presented to them. It isn’t straightforward to solve, since sometimes the process bounces, and miners are forced to shuffle and move to another problem.
Once the solution is found, the algorithm changes and becomes more complex. To explain Bitcoin further, it takes an average of ten minutes before miners bundle transactions together and release them to the blockchain as a valid block. If any of the miners picks John’s transaction, it gets validated, and Jane will receive the Bitcoin. Once the coins have successfully transferred, the wallet balances are updated.
Since the mining process is intensive, miners get rewarded with a fee for every block that’s added to the Bitcoin blockchain. The process is foolproof since transactions need to have emanated from the genesis block moving forward, and you can’t reverse a transaction after mining, since it will have to be broadcast throughout the network for authenticity.
How Does One Get Bitcoin?
Bitcoin’s skyrocketing price has brought the admiration of many investors and traders. So how do you earn Bitcoins? The following are the best ways to get Bitcoin:
- Buying from an exchange – There are a couple exchanges on the internet that accept fiat money for Bitcoin. However, there are also exchanges masquerading as genuine Bitcoin exchanges. It’s advisable to buy Bitcoin from established and reputable exchanges such as Coinbase, Kraken, and localBitcoins.
- Accept Bitcoins for goods and services – You can accept Bitcoin instead of fiat money whenever you sell goods or offer a service. An example is xbtfreelancer, which rewards freelancers with Bitcoin for freelance jobs. If you have a Shopify store online, you can accept Bitcoin whenever you make a sale. There is also a huge number of Bitcoin casinos in the USA. As more and more online services are becoming all about Bitcoin, it’s also now possible to accept it at your brick and mortar business.
- Mining – Miners get rewarded with 12.5 Bitcoin for every block they add to the blockchain. You can opt to buy the mining equipment and mine Bitcoin, or you can join a mining pool. You should know mining Bitcoin is capital intensive, and the process consumes a lot of electricity. Joining a mining pool would be a profitable alternative.
- Playing games online – You can participate in online games that reward players with millibit (mBTC), the smallest unit of Bitcoin. The games are 100% free to join, and you will be required to provide an email address and a Bitcoin account for receiving the mBTC.
How Is Bitcoin Stored?
Now that you know how to get Bitcoins, you will need a repository to hold them. There are three main ways to store Bitcoin.
- Paper wallet – Paper wallets are similar to cold wallets. However, with paper wallets, you will print the Bitcoin account address using an online wallet generator. Once you have the address printed, you can send Bitcoin to that address and store the printed paper. You can use the paper wallet as a gift or store it.
- Hot wallet – Hot wallets are Bitcoin wallets that are stored online. They have a similar approach to how emails are stored online. The convenience of hot wallets is that you can always retrieve your wallet(s), anytime, anywhere. However, their safety is less guaranteed since they’re prone to hacking. Despite having a strong password to your hot wallet account, the safety of your coins will also depend on the exchange security. Hot wallets are ideal for holding small Bitcoin amounts.
- Cold wallet – A cold wallet is a gadget that stores Bitcoin offline, and if you’re looking for information on the most secure way to store Bitcoins, this is it. Most times a cold wallet is a dongle, though sometimes it’s a hard drive. With a cold wallet, you need to keep it secure from theft or physical damage. Cold wallets are ideal to hold large Bitcoin amounts. An example of a cold wallet is Ledger Nano S. The picture below is a Bitcoin cold wallet (electroneum) that’s stored in a computer hard drive.
How to Use Bitcoin
Now that you learned how Bitcoins are generated, how you can acquire them, and how you can store them, let’s get to know how you can use Bitcoin. Bitcoin has the three properties of money: medium of exchange, unit of account, and store of value. However, what sets Bitcoin apart from fiat money is that the Bitcoin price fluctuates constantly and is hardly reliable as a store of value. The price volatility is why many businesses and individuals have stayed away from Bitcoin. However, there are some businesses that accept it. If you’re wondering what is Bitcoin used for, below is a list of businesses that accept Bitcoin:
- Microsoft – Microsoft accepts Bitcoin in the app store, and you can purchase games and movies.
- Buy Jewelry – stores such as APMEX, Sharps Pixley, and JM Bullion accepts Bitcoin in exchange for gold.
- Food – you can buy food from places like Subway, pizzaforcoins, and Burger King.
Book flights and accommodations – You can book a flight and hotel via Expedia and cheapair. - Online shopping – You can purchase some items online using Bitcoin. Popular online stores that accept Bitcoin are Shopify and Etsy.
- Online gambling – the anonymity of Bitcoin transactions has led to the rise of Bitcoin casinos. Many casino players would like their personal and financial information to be anonymous. Bitcoin gambling is a way players can achieve anonymity, making Bitcoin a choice for many players.
Adoption of BTC
The year 2017 saw Bitcoin’s price skyrocket from $1,000 and reach a high of almost $20,000 at its close. The rising price incentivized many people into purchasing Bitcoins. Merchants too had to bow to the pressure of accepting Bitcoin. The demand for Bitcoin rose and reached a market capitalization of over $200 billion USD in December 2017.
On the flipside, in that same year, Bitcoin’s adoption was hindered by governments banning Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. China banned Bitcoin trading and exchange operations, and similar sentiments were echoed by the governments of South Korea and Russia.
Advantages of Bitcoin
So what’s Bitcoin all about? Bitcoin blockchain architecture gives it several advantages compared to fiat currency. The whole idea of making Bitcoin transactions anonymous gives it an upper hand over fiat money, especially in online transactions.
- Anonymity – All Bitcoin transactions are anonymous. This is important especially for people who want to make transactions online without disclosing their personal information. Credit cards and other forms of fiat money are always traceable.
- Low transaction charges – Bitcoin transactions are low compared to the charges accrued from methods like bank transfers and bank wires. More so, the charges will depend on how fast you want the transaction to be processed. Priority is given to transactions that reward miners.
- Limited risk of inflation – Bitcoin circulation, by definition, is limited, since its mining gets harder over time, therefore reducing its supply. During a recession, governments print money to circulate back into the economy. There’s always a risk of inflation associated with an excess money supply.
- No third parties involved – Since Bitcoin operates in a decentralized environment, it’s hard for an entity to hold your Bitcoin unless they have access to your private key. Meanwhile, there are many reported cases of banks freezing individuals’ accounts.
Disadvantages of Bitcoin
The following are the disadvantages of Bitcoin.
- Irreversible transactions – Bitcoin transactions are irreversible. Once you send Bitcoins from your Bitcoin account, it’s impossible to reverse the transaction.
- Impossible to recover cold storage wallets – Once you lose or destroy a cold wallet; it’s impossible to recover the Bitcoins stored there.
- Bitcoin can be used for inappropriate dealings – the anonymous nature of Bitcoin and other decentralized cryptocurrencies gives room for illegal activities such as money laundering, online scams, and black market activities.
The Future of Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s future is hard to predict considering how Bitcoin is a technology byproduct and the last bubble (dotcom bubble) was technology related. Since we’ve been focusing on what is Bitcoin in the here and now, let’s also consider what Bitcoin may become.
The Promising Side
The Bitcoin community has always been pressuring for more innovation on the Bitcoin blockchain. With innovations such as Segwit, Proof of Work (POW), and the lightning network being the talk at this Bitcoin-focused online forum, it’s expected that the inherent weaknesses of Bitcoin will be addressed within the technology solutions proposed there.
The exposure and awareness Bitcoin has received from the media and social media channels are also good for its adoption. At the moment, a lot of people know what Bitcoins are, and this is good for its existence and its future.
The Problem Points
What is causing some concern with Bitcoin trading and mining has to do with government regulations. China used to be a world-leading country in Bitcoin transactions. However, due to the government’s ban on Bitcoin trading, it’s expected that the high volume will lower and people will shift to other things. Such measures limit the adoption and growth of Bitcoin. It’s hard for Bitcoin to revolutionize the finance industry with these regulations or stringent rules. After all, Satoshi’s Bitcoin idea was to create a decentralized money environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Who controls Bitcoin?
A: As explained earlier, Bitcoin operates in a decentralized environment, implying no entity controls Bitcoin. Bitcoin is run by the Bitcoin blockchain network. This represents a global network of computers, which are unassailable.
Q: Is it easy to use Bitcoin?
A: Using Bitcoin could be compared to using email. You need a sender’s address, the recipient address, and the internet. The same applies to Bitcoin. It’s first use may be a challenge; however, over time it becomes easy to use Bitcoin.
Q: How can I keep my wallet safe?
A: You should know that the passkey is the most important information for any Bitcoin account. It’s the difference between your Bitcoins being safe or stolen, so don’t disclose it to anyone and keep it safe. The passkey is irrecoverable.
Q: How much is one Bitcoin?
A: The forces of supply and demand determine the Bitcoin price. Once the demand for Bitcoin rises and its supply becomes limited, the price increases. The reverse is true. Exchanges are where supply and demand of Bitcoin is aggregated and the price is arrived at. You can check Bitcoin’s price on Coinbase, coinmarketcap, GDAX, and other cryptocurrency market-tracking sites.
Q: What is the limit I can send?
A: Bitcoin has no limit on how many coins you can send. As explained earlier in the section, “What Is Bitcoin?” it’s clear that Bitcoin transactions have no third-party oversight on who spends what amount of Bitcoin.